Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment Procedure
When there is an acute infection with no pus accumulation in & around the tooth, RCT can be completed in a single sitting. The biggest diagnostic aid, in this case, is an X-ray. The X-ray usually indicates the presence of pus accumulation in the form of a change (radiolucency) around the root tip of the involved tooth.
Advantages of single sitting RCT:
- Reduced patient’s appointment.
- Risk of inter appointment contamination and flare up chances.
- Reduced patient’s pain and fatigue.
- RCT treated tooth is more susceptible to crack during the process and single siting RCT minimizes the period between the start of RCT and the placement of a protective crown.
Steps in the Single Sitting RCT procedure:
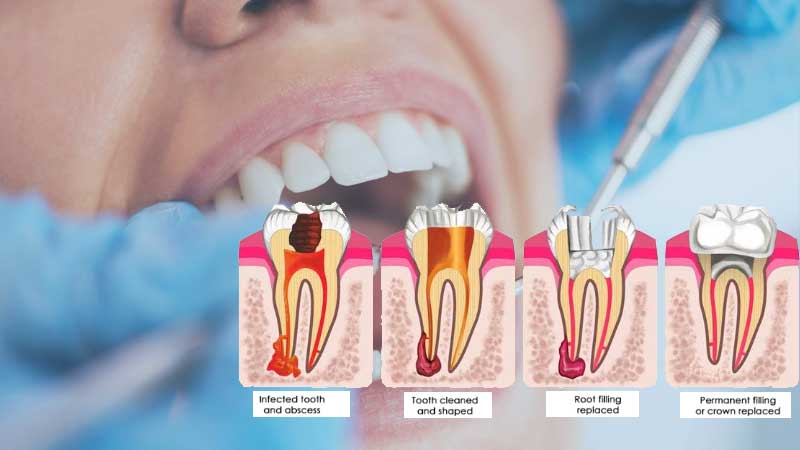
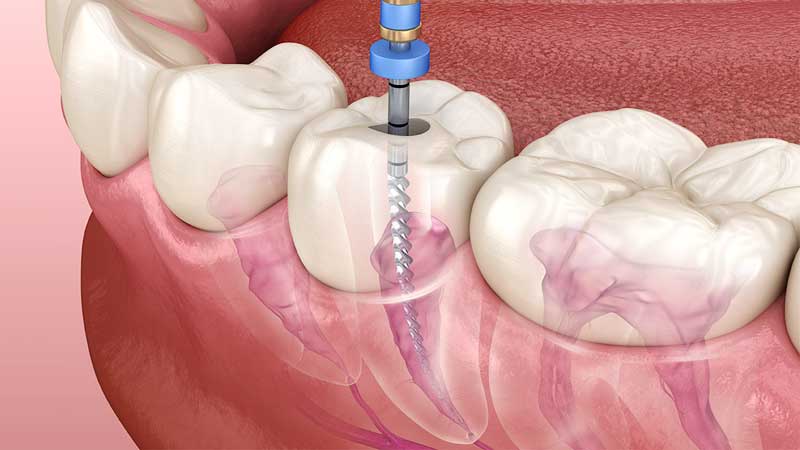
- The first step is to open the pulp chamber to allow access to the canals.
- Once open, with help of special instruments known as files the infected nerves is removed. The canals are flushed with an antiseptic solution.
- The root canals are further cleaned & reshaped to free them of all debris.
- Once the canals are empty dry & clean, they are filled and sealed with biocompatible material known as Gutta Purcha Points. / G.P. Points
- Radio-Visuo-Graphy (RVG), an advanced X-ray facility, is used to monitor and complete the treatment procedure to the desired level.
- The cavity is then filled with temporarily filling material which is then replaced with permanent filling material like composite filling.
- A root canal treated tooth should be ideally capped after 2 weeks.
Multiple-Sitting RCT Procedure
Not all the cases are suitable for a single sitting root canal, when there is a chronic/long-standing infection showing pus accumulation in & around the tooth without or with swelling abscess, RCT requires multiple sittings to drain the pus.
Steps in the Multi-sitting RCT procedure:
Stage I
The first step is to open the pulp chamber to allow access to the canals.
Once open, the infected nerves are removed with the help of special instruments known as files. The canals are flushed with an antiseptic solution. Sometimes frank discharge of pus can be seen oozing from canals along with foul odour. This should be flushed out.
The root canals are further cleaned & reshaped to free them of all debris.
The canals are dried & a temporary dressing is given. Root canal filling is not done.
Stage II
After a couple of days, the pulp chamber of the tooth is reopened. The canals are checked for discharge. If the canals are dry, RC filling is done.
If canals are still oozing, the canals are further cleaned & dried & a temporary dressing is given, without doing RC filling.
RC filling is done only in a subsequent sitting in which the canal is found dry and free of discharge. The number of sittings in such an RCT procedure can vary from case to case, depending on the nature of the infection.
Stage III
Once the RC filling is done, a temporary filling is done which is then replaced with permanent filling like composite filling.
In a chronic case, it may be advisable to wait for 2-3 months before the cap/crown procedure. This period ensures the complete healing of the tooth. Periodic X-rays give a good idea of the healing procedure. Once healed, the tooth should be capped.